Context

Network interconnects play an enabling role in HPC systems – and this will be even truer for the coming Exascale systems that will rely on higher node counts and increased use of parallelism and communication. Moreover, next-generation HPC and data-driven systems will be powered by heterogeneous computing devices, including low-power Arm and RISC-V processors, high-end CPUs, vector acceleration units and GPUs suitable for massive single-instruction multiple-data (SIMD) workloads, as well as FPGA and ASIC designs tailored for extremely power-efficient custom codes.
Network: the next big bottleneck?
These compute units will be surrounded by distributed, heterogeneous (often deep) memory hierarchies, including high-bandwidth memories and fast devices offering microsecond-level access time. At the same time, modern data-parallel processing units such as GPUs and vector accelerators can crunch data at amazing rates (tens of TFLOPS). In this landscape, the network may well become the next big bottleneck, similar to memory in single node systems.
RED-SEA prepares a new-generation network interconnect to power the future EU Exascale systems
RED-SEA will build upon the European interconnect BXI (BullSequana eXascale Interconnect), together with standard and mature technology (Ethernet) and previous EU-funded initiatives to provide a competitive and efficient network solution for the exascale era and beyond. This involves developing the key IPs and the software environment that will deliver:
- scalability, while maintaining an acceptable total cost of ownership and power efficiency;
- virtualization and security, to allow various applications to efficiently and safely share an HPC system;
- Quality-of-service and congestion management to make it possible to share the platform among users and applications with different demands;
- reliability at scale, because fault tolerance is a key concern in a system with a very large number of components;
- support of high-bandwidth low-latency HPC Ethernet, as HPC systems increasingly need to interact securely with the outside world, including public clouds, edge servers or third party HPC systems;
- support of heterogeneous programming model and runtimes to facilitate the convergence of HPC and HPDA;
- support for low-power processors and accelerators.

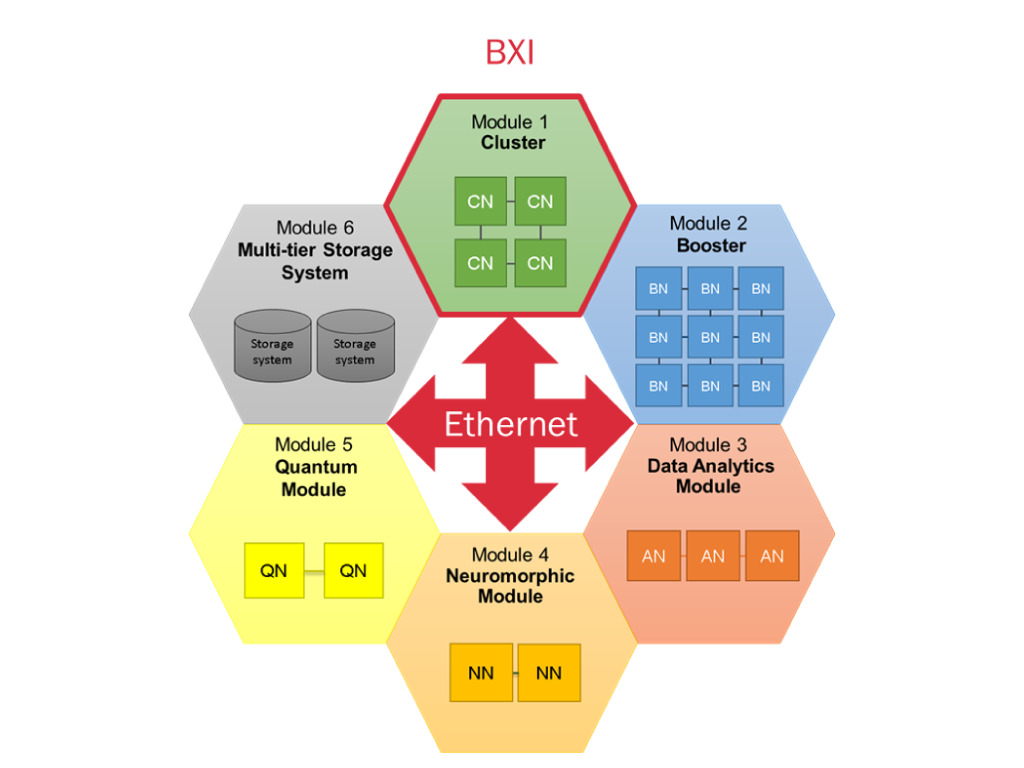
RED-SEA in the Modular Supercomputing Architecture
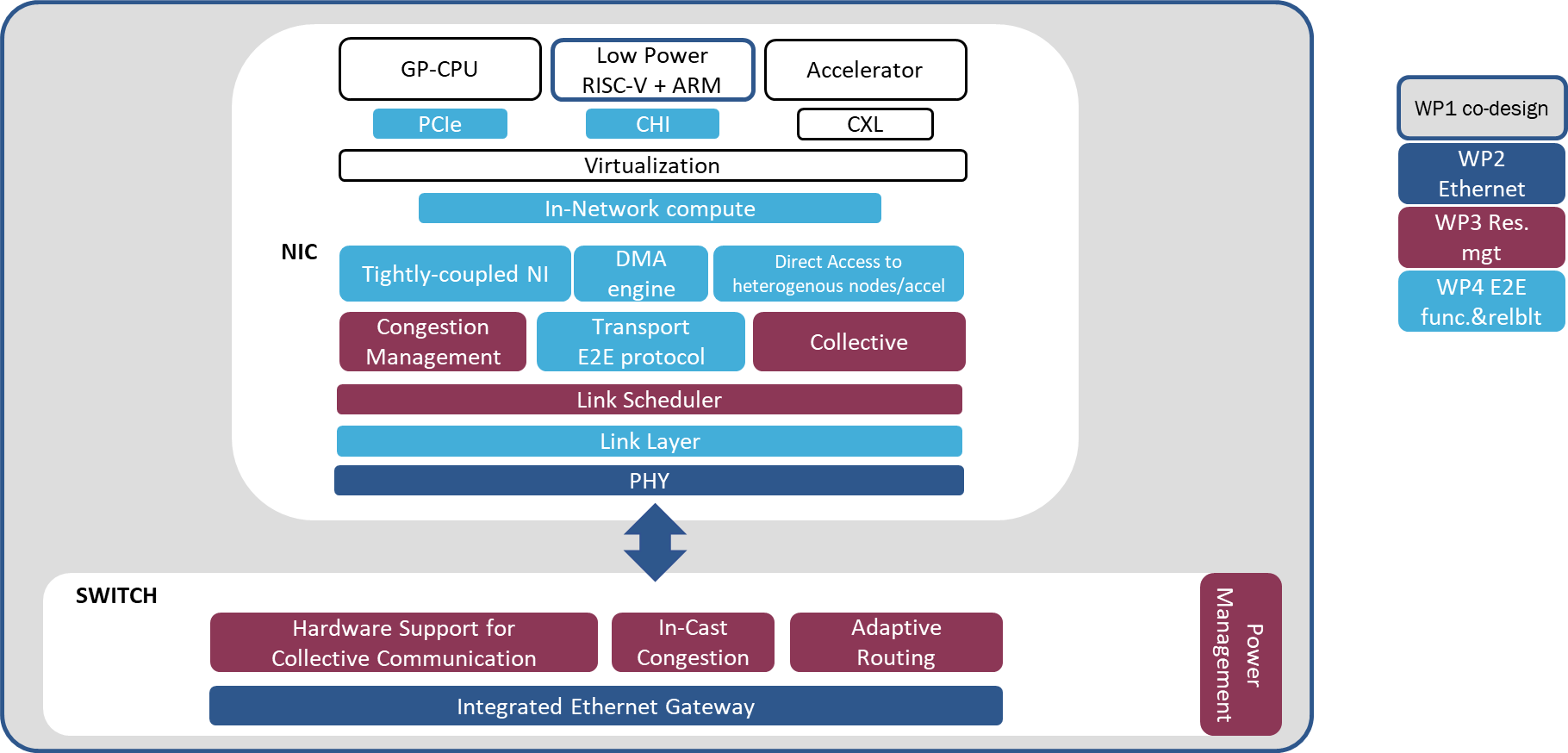
RED-SEA supports the Modular Supercomputing Architecture (MSA) that underpins all of the SEA projects. In the MSA, BXI is the HPC fabric within each compute module, delivering low-latency, high bandwidth and all required HPC features, whereas Ethernet is the high-performance federative network that offers interface to storage and with other compute modules. RED-SEA will design a seamless interface between BXI and Ethernet via a new Gateway solution.

Objectives
Enable
Enable the design of a new generation of high performance network interconnect
- Leveraging existing European technology (BXI, Exanest …)
- Able to power the future EU Exascale systems
Explore
Explore new innovative solutions
End-to-end network services – from programming models to reliability, security, low latency, and new processors
Develop
Develop the ecosystem and create a broader community of users and developers
Leveraging open standard and compatible API to develop innovative re-useable libraries and Fabrics management solutions
The RED-SEA network architecture
Partners
A consortium gathering academia and industry
The RED-SEA project is coordinated by Eviden (an Atos business), and brings together the top European academic centres and the key European industrial forces in the domain of interconnect networks. The RED-SEA consortium gathers 12 partners from 6 countries.
Collaborations
Technical collaborations with other projects are essential to ensure that technologies developed by RED-SEA actually get implemented and benefit users. Here are some examples.
- Collaboration between the DEEP-SEA and RED-SEA projects on VEF tracesAs part of its collaborations with other projects, RED-SEA sought to gather a wide array of network traces whose analysis will help provide recommendations for the design of the network system regarding latency, bandwidth in specific message size ranges, number of MPI messages and most relevant MPI calls to optimize. We have created a public… Read more: Collaboration between the DEEP-SEA and RED-SEA projects on VEF traces
- Collaborations between the IO-SEA and RED-SEA projectsMetrology and monitoring, optimization of data movements, cartography and in-depth knowledge of the network topology, interoperability, those are the fields identified by the IO-SEA and RED-SEA teams as having common points of interest for the two projects. Introduction IO-SEA (955811) and RED-SEA (955776) are two EuroHPC funded projects, belonging to the call EuroHPC-2019-1 topic b. … Read more: Collaborations between the IO-SEA and RED-SEA projects
Factsheet
| Project name | Network Solution for Exascale Architectures |
| Project acronym | RED-SEA |
| Project type | EuroHPC-RIA |
| Project start | 01/04/2021 |
| Project end | 31/03/2024 |
| Call | H2020-JTI-EuroHPC-2019-1 |
| Grant agreement | 955776 |
| Coordinator | Atos (Bull SAS) |
| Total budget | € 7 993 710 |
| EU funding | € 3 996 855,01 |
Deliverables
- D6.5 Final reportEdited by Claire Chen (BULL/Eviden) and Pascale Bernier-Bruna (BULL/Eviden) Executive summary The upcoming generation of Exascale systems is heavily reliant on a streamlined network infrastructure. This network must be capable of accommodating massively parallel processing… Read more: D6.5 Final report
- D5.5 Communication and Dissemination Final ReportEdited by Pascale Bernier-Bruna, Eviden (Bull SAS) Executive summary This report summarizes the communication and dissemination activities carried out throughout the life-time of the RED-SEA project, with special focus on the timeframe from October 2022… Read more: D5.5 Communication and Dissemination Final Report
- D1.4 Report on holistic evaluation of RED-SEA network technologiesEdited by N.Chrysos and V. Mageiropoulos (FORTH) Authors: all RED-SEA partners Executive summary In this deliverable, we summarize the key findings of technical and scientific results in the area of interconnection networks performed inside the… Read more: D1.4 Report on holistic evaluation of RED-SEA network technologies
- D2.9 BXI to Ethernet bridging demonstratorEdited by Damien Berton (Eviden / Bull SAS)) Executive summary This document D2.9 “BXI to Ethernet bridging demonstrator” is produced by Task T2.6 “BXI to Ethernet Gateway prototyping and testing”, which is part of Work… Read more: D2.9 BXI to Ethernet bridging demonstrator
- D4.7 Optimized MPI and compute in network implementationsEdited by Simon Pickartz (ParTec) Authors Xu Huang (ParTec), Simon Pickartz (ParTec), Carsten Clauss (ParTec), Gilles Moreau (CEA), Hugo Taboada (CEA), Marc Pérache (CEA), Timo Schneider (ETHZ) Executive summary This deliverable presents improvements of the… Read more: D4.7 Optimized MPI and compute in network implementations
- D2.3 RoCE and IPoverBXI Evaluation ReportEdited by Nikolaos D. Kallimanis (FORTH), Gregoire Pichon (Atos) Authors Giorgos Saloustros (FORTH), Nikolaos D. Kallimanis (FORTH), Nikolaos Chrysos (FORTH), Jonathan Espié Caullet (Atos), Sylvain Goudeau (Atos), Grégoire Pichon (Atos) Executive summary In the RED-SEA… Read more: D2.3 RoCE and IPoverBXI Evaluation Report
- D4.3 Planned MPI-related optimizationsEdited by Hugo Taboada (CEA) Authors Gilles Moreau (CEA), Hugo Taboada (CEA), Marc Pérache (CEA), Simon Pickartz (ParTec), Carsten Clauss (ParTec) Executive summary This document presents the two contributions from Commissariat à l’énergie atomique et… Read more: D4.3 Planned MPI-related optimizations
Publications
- Cppless: Productive and Performant Serverless Programming in C++This paper prepared by ETH Zürich was published in Arxiv. Abstract The rise of serverless introduced a new class of scalable, elastic and highly available parallel… Read more: Cppless: Productive and Performant Serverless Programming in C++
- User-guided Page Merging for Memory Deduplication in Serverless SystemsThis paper prepared by ETH Zürich was accepted at 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData). Abstract Serverless computing is an emerging cloud paradigm that… Read more: User-guided Page Merging for Memory Deduplication in Serverless Systems
- HEAR: Homomorphically Encrypted AllreduceThis paper prepared by ETH Zürich was accepted at SC23. Abstract Allreduce is one of the most commonly used collective operations. Its latency and bandwidth can… Read more: HEAR: Homomorphically Encrypted Allreduce
- Canary: Congestion-aware in-network allreduce using dynamic treesThis paper prepared by ETH Zürich was accepted in journal Future Generation of Computer Systems. Highlights Abstract The allreduce operation is an essential building block for many distributed… Read more: Canary: Congestion-aware in-network allreduce using dynamic trees
- Proyecto RED-SEA: Resultados IntermediosThis paper prepared by Universitat Politècnica de València and Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha was accepted and presented at conference XXXIII Jornadas de Paralelismo held from 20… Read more: Proyecto RED-SEA: Resultados Intermedios
- FMI: Fast and Cheap Message Passing for Serverless FunctionsThis paper was accepted at ICS ’23, the 37th International Conference on Supercomputing that was held from 21 to 23 June in Orlando, Florida, USA.… Read more: FMI: Fast and Cheap Message Passing for Serverless Functions
- FaaSKeeper: Learning from Building Serverless Services with ZooKeeper as an ExampleThis paper prepared by ETH Zürich was published on Arxiv. Abstract FaaS (Function-as-a-Service) brought a fundamental shift into cloud computing: (persistent) virtual machines have been replaced… Read more: FaaSKeeper: Learning from Building Serverless Services with ZooKeeper as an Example
- rFaaS: Enabling High Performance Serverless with RDMA and LeasesThis paper was accepted at IPDPS 2023, the 37th IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium that was held from 15 to 19 May in… Read more: rFaaS: Enabling High Performance Serverless with RDMA and Leases
- RED-SEA: Network Solution for Exascale ArchitecturesThis paper was accepted for the special session: “European Projects in Digital Systems Design (EPDSD) at the 25th Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD)… Read more: RED-SEA: Network Solution for Exascale Architectures
- Influence of Network Performance Variability on Application ScalabilityThis research paper prepared by ETH Zürich was published in the journal “Proceedings of the ACM on Measurement and Analysis of Computing Systems“. Abstract Cloud… Read more: Influence of Network Performance Variability on Application Scalability
- Building blocks for network-accelerated distributed file systemsResearch paper by our partner ETHZ, accepted at the SC22 Conference that took place online from 14 to 18 November 2022 in Dallas, TX, USA. This paper… Read more: Building blocks for network-accelerated distributed file systems
- NeVerMore: Exploiting RDMA Mistakes in NVMe-oF Storage ApplicationsResearch paper by our partner ETHZ, accepted at the ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS) that took place from 7 to 11 November… Read more: NeVerMore: Exploiting RDMA Mistakes in NVMe-oF Storage Applications
- Lifting C semantics for dataflow optimizationResearch paper by our partner ETHZ, accepted at the ICS ’22 International Conference on Supercomputing that took place online from 28 to 30 June 2022.… Read more: Lifting C semantics for dataflow optimization
- KafkaDirect: Zero-copy Data Access for Apache Kafka over RDMA NetworksResearch paper presented at the ACM SIGMOD/PODS Conference that took place in Philadelphia from 12 to 17 June 2022. Abstract Apache Kafka is an open-source… Read more: KafkaDirect: Zero-copy Data Access for Apache Kafka over RDMA Networks
- Asynchronous Distributed-Memory Triangle Counting and LCC with RMA CachingThis paper was accepted at IPDPS 2022, the 36th IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium that was held from 30 May to 03 June… Read more: Asynchronous Distributed-Memory Triangle Counting and LCC with RMA Caching
- Optimized Page Fault Handling During RDMAThis research paper was accepted by the journal IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems and will be published in vol. 33, no. 12, pp.… Read more: Optimized Page Fault Handling During RDMA
- A RDMA Interface for Ultra-Fast Ultrasound Data-Streaming over an Optical LinkResearch paper presented at the DATE 2022 conference (Design, Automation and Test in Europe conference) that took place online from 14 to 23 March 2022.… Read more: A RDMA Interface for Ultra-Fast Ultrasound Data-Streaming over an Optical Link
- Flare: flexible in-network allreduceResearch paper presented at the SC21 conference (St Louis, USA and online) Abstract The allreduce operation is one of the most commonly used communication routines in distributed… Read more: Flare: flexible in-network allreduce
- A RISC-V in-network accelerator for flexible high-performance low-power packet processingResearch paper presented at the ISCA 2021 conference (online) Abstract The capacity of offloading data and control tasks to the network is becoming increasingly important,… Read more: A RISC-V in-network accelerator for flexible high-performance low-power packet processing